Abstract
Background: During inpatient treatment of patients (pts) with blood diseases (BD) severe neurological complications (SNC) can occur, which lead treatment protocol interruption.
Objective: Determine the types, frequency, symptoms, and predictors of SNC that occurred during inpatient treatment of pts with BD.
Patients and Methods: The retrospective exploratory study was conducted on the data analysis of 3,620 pts with BD who were undergoing inpatient treatment from 01. 2018 to 12.2019 in the National Research Center for Hematology (Moscow). 34 pts (with diagnoses: lymphoid neoplasms - 67.7%, myeloid neoplasms - 26.5%, others BD - 5.9%) those who had SNC, were selected: 14 men and 20 women, median age 39 years, interquartile range (IQR): 33-55 years. The neurological complication was estimated as SNC if it was an indication for transition to the intensive care unit. In order to reveal the predictors associated with the development of SNC, the pts who had SNC, were compared with the comparison group of 137 pts (formed using the Kernel matching method) who were similar to the main group by clinical and laboratory characteristics: 59 men and 78 women, median age 36 years, IQR: 26-53 years. Statistical analysis included the multivariate analysis: multiple binary logistic regression with stepwise inclusion of variables (that were found in the preliminary contingency table analysis), control false results (by the false discovery rate method) and odds ratio, OR (95% confidence interval), estimation.
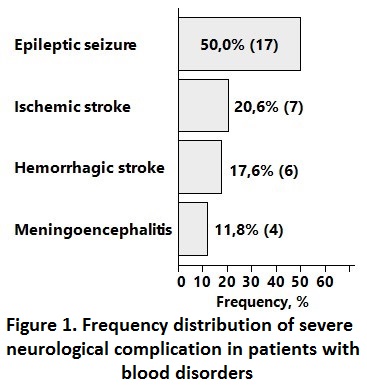
Results: SNC in pts with BD, developed in 0.94% of cases. The main SNC in pts with BD were:
• epileptic seizure (50.0%, n=17),
• ischemic stroke (20.6%, n=7),
• hemorrhagic stroke (17.6%, n=6),
• and meningoencephalitis (11.8%, n=4) (Figure 1).
The following independent statistically significant (Wald test, p≤0.05) predictors associated with the development of SNC in pts with BD during the treatment, were identified:
• antibiotic therapy (when more than 5 drugs are prescribed), OR = 2.9 (1.2-7,4);
• chemotherapy (when more than 4 drugs are prescribed), OR = 2.9 (1.1-7.8);
• thrombocytopenia (with a platelet count less than 50 x 10 9 g/l), OR = 2.3 (1.0-5.2);
• the development of delirium in the pts, OR = 3.7 (1.3-10.8);
and also the risk factor:
• neurological disorders in the pts's medical history, OR = 2.6 (1.1-6.3).
Conclusion. In the process of inpatient treatment pts with BD may develop SNC. This life-threatening complication violates the intended therapeutic protocol, which affects the results of BD treatment in general. The main types of SNC detected were: epileptic seizure, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, and meningoencephalitis. Four predictors such as massive antibacterial (more than 5 drugs prescribed) and chemotherapeutic effects (more than 4 drugs prescribed), thrombocytopenia and manifestation of delirium, associated with the development of SNC in pts with BD in the process of treatment, as well as one risk factor (the presence of neurological disorders in the patient checked-in history) were identified. All these independent signs must be taken into account and monitored in the treatment, as each of them increases the risk of the SNC development.
Zakharov: Takeda: Honoraria; EverNeuroPharma: Honoraria; KanonPharma: Honoraria; Merz: Honoraria; Boerhinger Ingelheim: Honoraria; Abbot: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Egis: Honoraria; Polysan: Honoraria; SCS: Honoraria; Pharmasoft: Honoraria; Valenta: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal